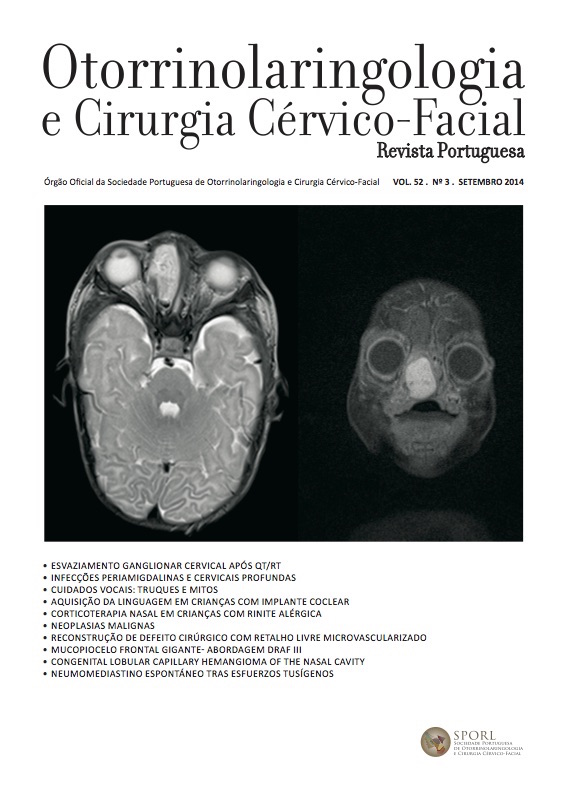
Peritonsillar and deep neck infections - Prospective study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.34631/sporl.447Keywords:
tonsillar abscess, deep cervical infection, antibiotic therapy, infectious agentsAbstract
Objectives: To evaluate and establish a relation of the demographic, symptomatic, analytical, microbiological and outcome characteristics of hospitalized patients with peritonsillar and deep neck infection.
Material and methods: A prospective study of patients admitted to the Hospital of Guimarães from March 2011 to March 2012 with the diagnosis of peritonsillar or deep neck infection.
Results: During the study period 47 patients were hospitalized, 24 males and 23 females. The average age of the patients was 31.7 ± 17.3 years. A total of 24 microbiological cultures were carried out. Most abscesses had group A beta-hemolytic streptococci etiology.
Conclusions: The data are consistent with the literature. The study highlights the importance of the elimination of risk factors for these infections. The value of C reactive protein and the type of infection is correlated with the duration of hospitalization.
Downloads
References
Suehara AB, Gonçalves AJ, Alcadipani FC, Kavabata NK, et al. Infecções cervicais profundas: análise de 80 casos. Rev Bras
Otorrinolaringol. 2008; 74:253-9.
Wang LF, Kuo WR, Tsai SM, Huang KJ. Characterizations of life threatening deep cervical infections: a review of one hundred ninetysix cases. AM J Otolaryngol. 2003; 24:111-7.
Chen MK, When YS, Chang CC, Huang MT. Predisposing factors of life-threatening deep neck infection: logistic regression analysis of 214 cases. AM J Otolaryngol 1998; 27:141-4.
Pereira S, Martins JA, Novas AC, Montemor R, et al. Infecções cervicais - Casuística dum serviço de ORL. Rev. Port. de ORL e Cir. Cerv. Facial 2011; 49:139-45
Sennes L, Imamura R, Junior FV, Simoceli L, et al. Infecções dos espaços cervicais: estudo prospectivo de 57 casos. Rev Bras de Otorrinolaringol. 2002; 68:388-93
Parhiscar A, Har-El G. Deep neck abcess: a retrospective review of 210 cases. Ann Oto Rhinol Laryngol 2001; 110:1051-4
Garcia JM, Zavarce IH, Costa AS, Macía OC. Abscesso periamigdalino: Incidencia y manejo actual. Rev. Port. de ORL e Cir. Cerv. Facial 2011; 49:147-50
Ferreira M, Brito MJ, Machado MC. Abcessos faríngeos. Acta Pediatr Port 2008; 39:62-5
Lee YQ, Kanagalingam J. Bacteriology of deep neck abscesses: a retrospective review of 96 consecutive cases. Singapore Med J 2011; 52(5):351
Ogubtebi B, Slee AM, Tanzer M, Langelan K. Predominant Microflora Associated with Human Dental Periapical Abscesses. J.
Clin.Microbiol. 1982; 15:964–969
Hall SF. Peritonsillar abscess: the treatment options. AM J Otolaryngol 1990;19:226-29
Liu SA, Liaang MT, Wang CP, Wang CC et al. Pre-operative blood sugar and C-reactive protein associated with persistent discharge after incision and drainage for patients with deep neck abscess. Clin Otolaryngol. 2009; 34(4): 336-42
Ohata A, Kikuchi S, Yohinami H, Takegoshi et al. Clinical study on deep neck infection; J Otolaryng Jap 2006; 109(7): 587-93