Giant frontal mucopyocele: Draft III approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.34631/sporl.453Keywords:
Mucocele, Mucopyocele, Endoscopic Sinus Surgery, Modified Lothrop, Draf IIIAbstract
Mucoceles are mucous-filled cystic lesions of the paranasal sinuses that can result in bone erosion with extracranial, intracranial or orbital extension. They are denominated mucopyocele if there is infection of the mucous filling. The surgical approach when they are localized in the frontal sinus is a challenge for the ENT surgeon; some authors prefer exclusively endoscopic techniques that go from marsupialization to Draf III procedures, while others advocate combined osteoplastic approaches.
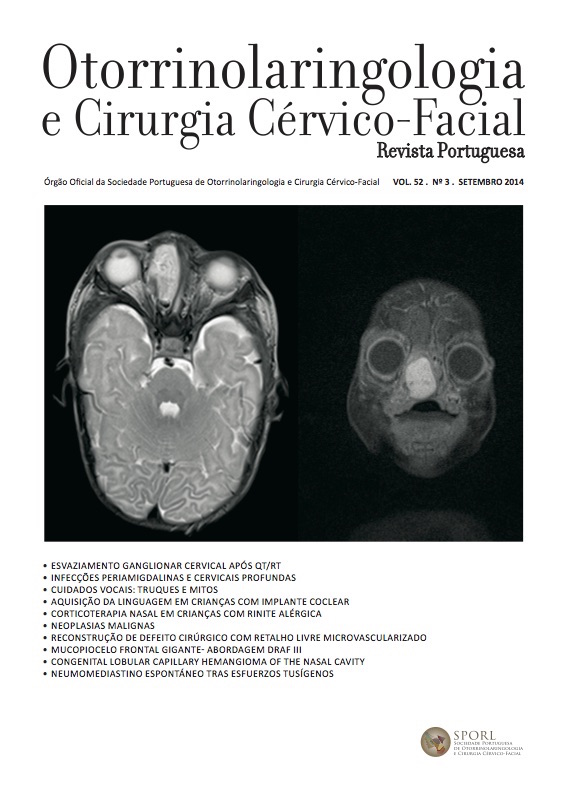
We report a case of 74 year-old man who presented at our hospital center (CHAA) outpatient clinic with right frontal tumefaction with 10 month evolution and slow growing. After imagiological study, it was established the diagnosis of a giant frontal mucocele. The patient was submitted to endoscopic sinus surgery, through a Draf type III frontal sinusotomy, without any complications.
After one-year follow-up, there were no symptoms or clinical, endoscopic or imagiological signs of mucocele recurrence.
Downloads
References
-Vicente A, Chaves A, Takahashi E et al. Frontoethmoidal mucoceles: a case report and literature review. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol, 2004;70(6): 850-4.
-Belirti A, Olgusu V, Olgu N. Frontal Mucocele Presenting with Forehead Subcutaneous Mass: an unusual presentation. Turkish
Neurosurgery, 2008;18(2): 200-3.
-Dispenza C, Saraniti C, Caramanna C et al. Endoscopic treatment of maxillary sinus mucocele. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2004
Oct;24(5):292-6.
-Suri A, Mahapatra A, Gaikwad S et al. Giant Mucoceles of the frontal sinus: a series and review. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience,
;11(2): 214.
-Sautter N, Citardi M, Pery J et al. Paranasal sinus mucoceles with skull-base and/or orbital erosion: Is the endoscopic approach
sufficient? Otolaryngol Head and Neck Surgery, 2008;139: 570-4.
-Herndon M, McMains K, Kountakis S. Presentation and management of extensive fronto-orbital-ethmoid mucoceles. American J of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Medicine and Surgery, 2007;28: 145-7.
-Lund VJ, Henderson B, Song Y. Involvement of cytokines and vascular adhesion receptors in the pathology of fronto-ethmoidal mucoceles. Acta Otolaryngol,1998; 113:540-5.
-Sakae F, Filho B, Lessa M et al. Bilateral Frontal Sinus Mucocele. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol, 2006;72(3): 428.
-Hardy M, Montgomery W. Osteoplastic frontal sinusotomy: an analysis of 250 operations. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 1976;85(4):523-532.
-Anderson P, Sindwani R. Safety and Efficacy of the Endoscopic Modified Lothrop Procedure. Laryngoscope, 2009;119: 1828.
-Weber R, Draf W, Keerl R et al. Osteoplastic Frontal Sinus Surgery with Fat Obliteration. Laryngoscope, 2000;110: 1037.
-Kennedy DW, Josephson JS, Zinreich SJ et al. Endoscopic sinus surgery for mucoceles: a viable alternative. Laryngoscope, 1989;99: 885.
-Draf W, Weber R. Endonasal pansinus operation in chronic sinusitis. Indication and operation technique. Am J Otolaryngol, 1993;14: 394-398.
-Draf W. The frontal sinus. Scott’s Brown Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, 7th edition. Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd; 2008
-Friedel M, Li S, Langer PD et al. Modified Hemi-Lothrop Procedure for Supraorbital Ethmoid Lesion Access. Laryngoscope, 2012;122:443-444.