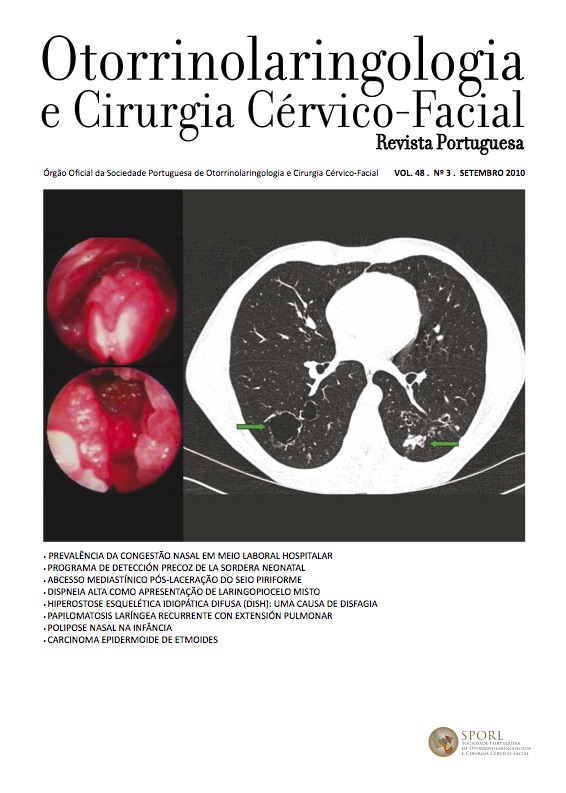
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with pulmonary extension
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.34631/sporl.227Keywords:
Cidofovir, pulmonary papillomatosis, laryngeal microsurgery, laser CO2, human papilloma virusAbstract
Introduction: Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is a chronic disease that is characterized by the proliferation of benign exofitic lesions within the superior respiratory tract, most often in vocal cords. In about 30% of cases tends to spread to the inferior respiratory and digestive tracts.
Case Report: A 37 year old man was diagnosed with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis at age of five. Since then he has been undergone laryngeal microsurgery for 42 times with complementary adjuvant therapy with intron-A and cidofovir. Seven years ago the disease affected the pulmonary parenchima, a very uncommon complication that overshadows the evolution of the disease.
Discussion: This disease is often difficult to treat and control because of the recurrence and the extension to aerodigestive tract. At moment, there is no treatment to cure the papillomatosis. The laser CO2 with intralesional injection of cidofovir are currently the most used techniques.
Downloads
References
Mascareñas de los Santos A, Ortiz de la Peña A, Cruz A, Sams S. Virus del Papiloma Humano. Revista de enfermedades infecciosas en Pediatría 2007; Vol XX Num 80.
Silverberg M, Thorsen P, Lindeberg H, Grant L et al. Condyloma in Pregnancy is strongly Predictive of juvenile onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Am Coll Obstetr Gynecol. April 2003; 101(4): 645-52.
Lupiani MP, Fraga ME Vacuna del virus del papiloma humano: se amplia el calendario vacunal. Canar Ped 2008; 32(1): 11-16.
Gerein V, Rastorguev E, Gerein J, et al. Incidence, age at onset, and potential reasons of malignan transformation in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis patients: 20 years experience. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;132:392-394.
Ruan S, Chen K, Yang P. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with pulmonary involment: A case report and review of the literature. Respirology 2009;14:137-140.
Derkay C, Wiatrak B. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Review. The Laryngoscope 2008;118:1236-47.
Preuss SF, Klussmann JP, Jungehulsing M, et al. Long-term results of surgical treatment for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 2007; 127:1196-1201.
Brunetto B, Zelada Ursula. Uso del cidofovir en la papilomatosis respiratoria recurrente. Rev. Otorrinolaringol. Cir. Cabeza Cuello 2007; 67:153-156.
Castillo P, García R, Flores S, Núñez C. Tratamiento combinado de la Papilomatosis laringotraqueal con láser ND- YAG y cidofovir intralesional. Neumología y Cirugía de Tórax 2005;64(1):30-33.
Zabawski EJ Jr. A review of topical and intralesional cidofovir. Dermatology Online J 2000;6(1):3
Broekema F, Dikkers F. Side-effects of cidofovir in the treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2008;265:871-879.
Gillison M, Chauturvedi A, Lowy D. HPV Prophylactic vaccines and the potential prevention of noncervical cancers in both men and women. Cancer Supplement 2008;113(10):3036-46.
Sidhu TS, Sharma AK, Sharma N, et al. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007 Feb;136(2):321-3
Bonilla M, Barrientos J.C, Ferrera A. Caracterización clínico-epidemiológica e identificación molecular del virus papiloma humano en papilomatosis respiratoria recurrente. Revista Médica de los PostGrados de Medicina 2008; 11(1):
-61.