Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): A cause of dysphagia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.34631/sporl.228Keywords:
Dysphagia, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis, DISHAbstract
Dysphagia is an important symptom, usually non-specific, meaning difficulty in swallowing. A possible cause of dysphagia is Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH), a disorder characterized by calcification and ossification of the soft tissue, namely of the ligaments and tendons.
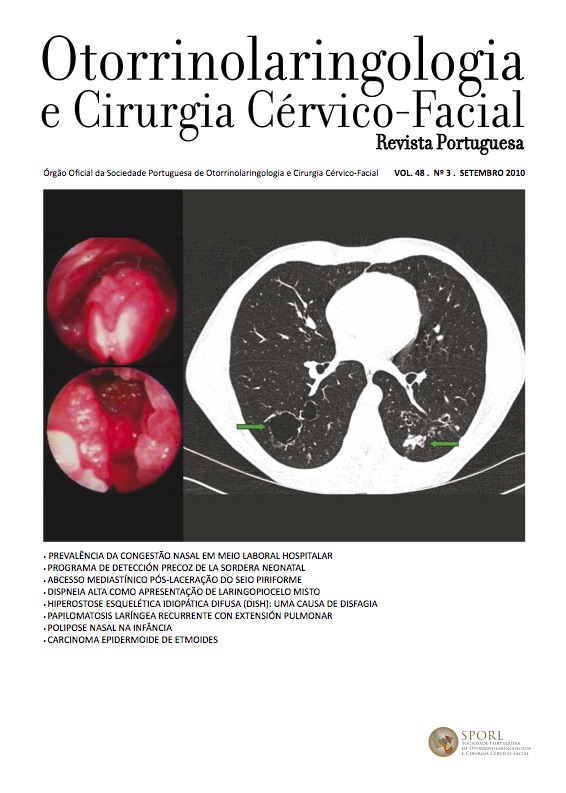
We report a case of a 58 year old man with a 4 month history of dysphagia for solids, referred to the ER by a Gastroenterologist for an urgent ENT consult due to lack of progression of the endoscope at the hypopharynx.
A thorough ENT examination verified a protrusion in the left posterior lateral wall of the pharynx obscuring the ispilateral piriform sinus. The CT scan showed calcification of the anterior common longitudinal ligament from C2 to C6 and anterior marginal sclerosis, more exuberant in C3 and C4, deforming the posterior wall of the pharynx. Thus the diagnosis of DISH was obtained.
Downloads
References
Mader R. Clinical Manifestations of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis of the Cervical Spine. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2002;32(2):130-135.
Boachie-Adjei O, Bullough P. Incidence of ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine (Forestier’s disease) at autopsy. Spine, 1987;12:739-43.
Rotes-Querol J. Clinical manifestations of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Br J Rheumatol, 1996;35:1193-6.
Foshang TH, Mestan MA, Riggs LG. Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis: A Case of Dysphagia. J Manipulative Physiol Ther, 2005;25: 71-76.
Cammisa M, De Serio A, Guglielmi G. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Eur J Radiol (Suppl) 1998;27: S7-S11.
Kmucha ST, Cravens RB. DISH syndrome and its role in dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1994;110:431-6.
Akhtar S, O’Flynn PE, Kelly A, Valentine PM. The management of dysphagia in skeletal hyperostosis. J Laryngol Otol,/2000;114:154-7.
Mata S, Chhem RK, Fortin PR, et al. Comprehensive radiographic evaluation of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: Development and interrater reliability of a scoring system. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 1998;28:88-96.
Resnick D. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1995:pp.1463-95.