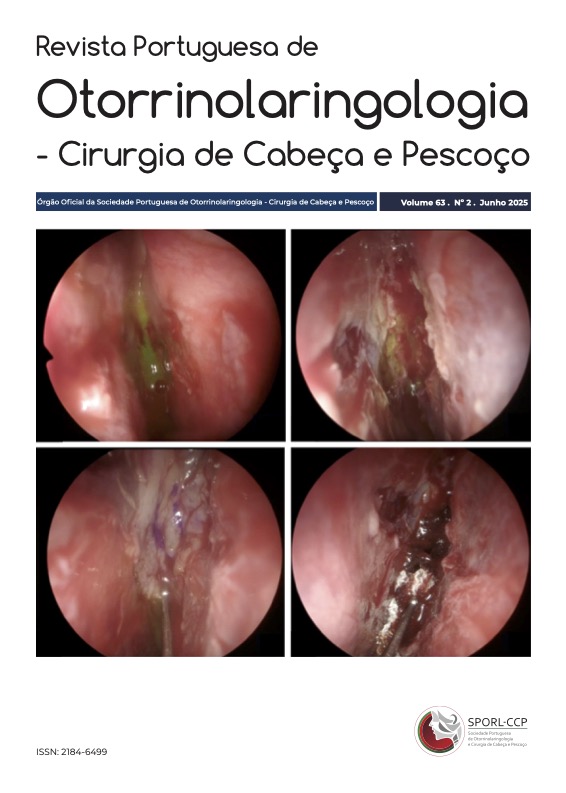
Fáscia temporoparietal e placas de polidioxanona (PDS), a solução para as perfurações septais?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.34631/sporl.2178Palavras-chave:
Perfuração septal, polidioxanona, cirurgiaResumo
Introdução: As perfurações septais permanecem um desafio cirúrgico e têm sido desenvolvidas novas abordagens e técnicas no sentido de otimizar a taxa de encerramento. Quando sintomáticas, as perfurações podem causar obstrução nasal ou epistáxis recorrente, necessitando de tratamento. Este estudo relata dois casos clínicos de perfurações septais sintomáticas.Objetivo: Descrever o diagnóstico, tratamento e resultados cirúrgicos, acompanhado por registos fotográficos do seguimento e comparar os resultados com a literatura existente.
Materiais e Métodos: Dois pacientes foram submetidos a cirurgia usando uma combinação de placas de polidioxanona (PDS) de 0,25mm e fáscia temporoparietal.
Resultados: Dois casos clínicos foram tratados com sucesso usando uma abordagem fechada, incisão hemitransfixante direita e um enxerto combinado de PDS e fáscia temporoparietal. Foi obtido o encerramento completo das perfurações e resolução da sintomatologia associada.
Conclusão: A técnica combinada de PDS e fáscia temporoparietal demonstrou alta eficácia, sugerindo sua utilidade no tratamento de perfurações septais sintomáticas.
Downloads
Referências
Morse J, Harris J, Owen S, Sowder J, Stephan S. Outcomes of nasal septal perforation repair using combined temporoparietal fascia graft and polydioxanone plate construct. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2019 Jul 1;21(4):319-326. doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2019.0020.
Pereira C, Santamaría A, Langdon C, López-Chacón M, Hernández-Rodríguez J, Alobid I. Nasoseptal perforation: from etiology to treatment. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018 Feb 5;18(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11882-018-0754-1.
Flavill E, Gilmore JE. Septal perforation repair without intraoperative mucosal closure. Laryngoscope. 2014 May;124(5):1112-7. doi: 10.1002/lary.24386.
Alobid I. Endoscopic approach for management of septal perforation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Aug;276(8):2115-2123. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05490-w.
Lindemann J, Goldberg-Bockhorn E, Scheithauer MO, Hoffmann TK, Sommer F, Stupp F. et.al. A contemporary review of “realistic” success rates after surgical closure of nasal septal perforations. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2021 Dec;48(6):1039-1046. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2021.03.013.
Epprecht L, Schlegel C, Holzmann D, Soyka M, Kaufmann T. Closure of nasal septal perforations with a polydioxanone plate and temporoparietal fascia in a closed approach. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2017 May 1;31(3):190-195. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2017.31.4431.
Sand JP, Desai SC, Branham GH. Septal perforation repair using polydioxanone plates: a 10-Year comparative study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015 Oct;136(4):700-703. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001571.
Rimmer J, Saleh H. Use of polydioxanone plate in septal reconstruction. Facial Plast Surg. 2013 Dec;29(6):464-72. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1360591.
Pignatari S, Nogueira JF, Stamm AC. Endoscopic "crossover flap" technique for nasal septal perforations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 Jan;142(1):132-134.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2009.08.024.
Rusetsky Y, Mokoyan Z, Spiranskaya O, Arutyunyan S. Cross-septal returned flap: modified endoscopic technique for bilateral closure of septal perforation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020 Oct;49(10):1260-1263. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2020.01.026.
Altun H, Hanci D. Olfaction improvement after nasal septal perforation repair with the “cross-stealing” technique. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015 Sep-Oct;29(5):e142-5. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4208.
Boenisch M, Nolst Trenité GJ. Reconstruction of the nasal septum using polydioxanone plate. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2010 Jan-Feb;12(1):4-10. doi: 10.1001/archfacial.2009.103.
Kim SW, Rhee CS. Nasal septal perforation repair: predictive factors and systematic review of the literature. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012 Feb;20(1):58-65. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e32834dfb21.
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Secção
Licença
Direitos de Autor (c) 2025 Catarina Martins Pinto, Ricardo Matos, Margarida Martins, Clara Mota, Mariana Santos, Duarte Morgado, Rui Fonseca

Este trabalho encontra-se publicado com a Licença Internacional Creative Commons Atribuição-CompartilhaIgual 4.0.