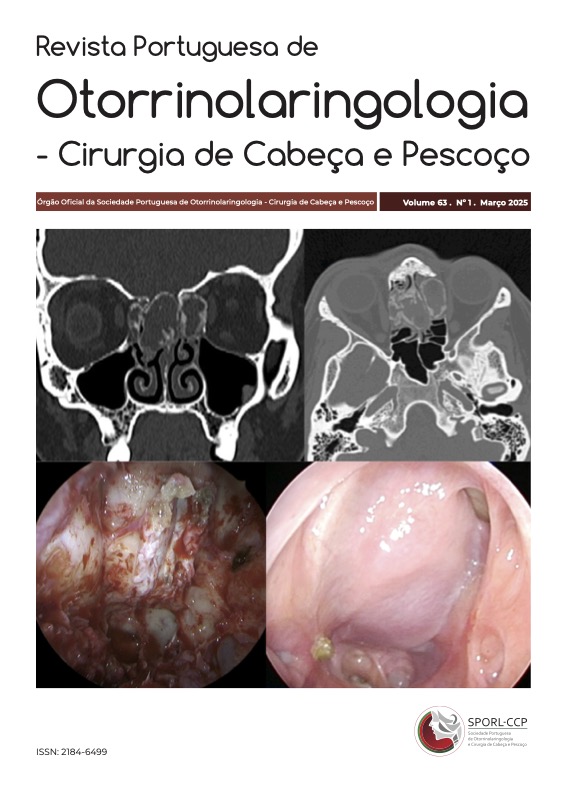
Sacadas corretivas com ganho normal do RVO no Schwannoma Vestibular
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.34631/sporl.3064Palavras-chave:
Schwannoma Vestibular, Video Head Impulse Test, Sacadas Corretivas, Reflexo Vestibulo-OcularResumo
O Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) é usado para avaliar a função vestibular. Esta ferramenta tem-se mostrado valiosa em pacientes com Schwannoma Vestibular (VS).
Apresentamos um caso de um homem de 64 anos com SV de 6mm no canal auditivo interno esquerdo, detetado acidentalmente numa Ressonância Magnética cerebral. O paciente negou apresentar qualquer sintoma vestibular ou auditivo. O exame físico revelou hipoacusia neurossensorial esquerda ligeira e teste de impulso cefálico positivo para a esquerda. O vHIT mostrou um valor normal de ganho do reflexo vestíbulo-ocular (RVO) em todos os canais semicirculares (CSCs), apesar da presença de sacadas corretivas (SCs) evidentes ao testar os CSCs lateral e posterior esquerdos.
O vHIT é uma ferramenta valiosa para avaliar a função vestibular. Em pacientes com valores normais de ganho de VOR, défices subtis na função dos CSCs podem ser detetados através da presença de SCs, indicando a importância da incorporação do vHIT em avaliações diagnósticas de rotina de pacientes com distúrbios vestibulares
Downloads
Referências
Halmagyi GM, Chen L, MacDougall HG, Weber KP, McGarvie LA, Curthoys IS. The Video Head Impulse Test. Front Neurol. 2017 Jun 9:8:258. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00258.
Macdougall HG, McGarvie LA, Halmagyi GM, Curthoys IS, Weber KP. The video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) detects vertical semicircular canal dysfunction. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 22;8(4):e61488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061488.
Fujiwara K, Yanagi H, Morita S, Hoshino K, Fukuda A, Nakamaru Y. et al. Evaluation of vertical semicircular canal function in patients with Vestibular Schwannoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2019 Feb;128(2):113-120. doi: 10.1177/0003489418808545.
MacDougall HG, Weber KP, McGarvie LA, Halmagyi GM, Curthoys IS. The video head impulse test: diagnostic accuracy in peripheral vestibulopathy. Neurology. 2009 Oct 6;73(14):1134-41. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bacf85.
Yang CJ, Lee JY, Kang BC, Lee HS, Yoo MH, Park HJ. Quantitative analysis of gains and catch-up saccades of video-head-impulse testing by age in normal subjects. Clin Otolaryngol. 2016 Oct;41(5):532-8. doi: 10.1111/coa.12558.
Agrawal Y, Van de Berg R, Wuyts F, Walther L, Magnusson M, Oh E. et al Presbyvestibulopathy: diagnostic criteria Consensus document of the classification committee of the Bárány Society. J Vestib Res. 2019;29(4):161-170. doi: 10.3233/VES-190672.
Myrseth E, Møller P, Wentzel-Larsen T, Goplen F, Lund-Johansen M. Untreated vestibular schwannomas: vertigo is a powerful predictor for health-related quality of life. Neurosurgery. 2006 Jul;59(1):67-76; discussion 67-76. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000219838.80931.6B.
Curthoys IS. Vestibular compensation and substitution. Curr Opin Neurol. 2000 Feb;13(1):27-30. doi: 10.1097/00019052-200002000-00006
Brown CS, Peskoe SB, Risoli T Jr, Garrison DB, Kaylie DM. Associations of video head impulse test and caloric testing among patients with Vestibular Schwannoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Aug;161(2):324-329. doi: 10.1177/0194599819837244.
Nam GS, Bae SH, Kim HJ, Cho JW, Moon IS. Feasibility of preoperative video head impulse test to predict the nerve of origin in patients with Vestibular Schwannomas. J Clin Med. 2021 Jun 17;10(12):2677. doi: 10.3390/jcm10122677.
van Esch BF, Nobel-Hoff GE, van Benthem PP, van der Zaag-Loonen HJ, Bruintjes TD. Determining vestibular hypofunction: start with the video-head impulse test. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Nov;273(11):3733-3739. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4055-9.
Crane BT, Demer JL. Latency of voluntary cancellation of the human vestibulo-ocular reflex during transient yaw rotation. Exp Brain Res. 1999 Jul;127(1):67-74. doi: 10.1007/s002210050774.
Shen Q, Magnani C, Sterkers O, Lamas G, Vidal PP, Sadoun J. et al. Saccadic velocity in the new suppression head impulse test: a new indicator of horizontal vestibular canal paresis and of vestibular compensation. Front Neurol. 2016 Sep 23:7:160. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00160.
Kabaya K, Fukushima A, Katsumi S, Minakata T, Iwasaki S. Presence of corrective saccades in patients with normal vestibulo-ocular reflex gain in video head impulse test. Front Neurol. 2023 Apr 13:14:1152052. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1152052.
Rambold HA. Age-related refixating saccades in the three-dimensional video-head-impulse test: source and dissociation from unilateral vestibular failure. Otol Neurotol. 2016 Feb;37(2):171-8. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000947.
Schubert MC, Hall CD, Das V, Tusa RJ, Herdman SJ. Oculomotor strategies and their effect on reducing gaze position error. Otol Neurotol. 2010 Feb;31(2):228-31. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181c2dbae.
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Secção
Licença
Direitos de Autor (c) 2025 Os autores mantêm os direitos de autor deste artigo.

Este trabalho encontra-se publicado com a Licença Internacional Creative Commons Atribuição-CompartilhaIgual 4.0.